GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
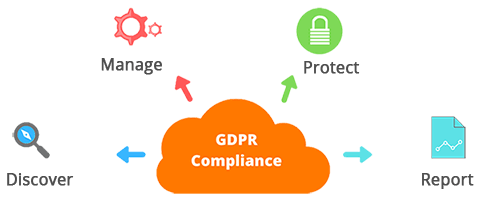
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union (EU) regulation for data protection. It applies to businesses’ processing of personal data from people in the EU regions. The regulation pertains to the full data life cycle, from gathering and storage to usage and retention. It is important to note that GDPR applies not only to firms based in the EU, but any organization providing a product or service to residents of the EU – and that in the event of data breaches, GDPR creates the potential for headline-grabbing penalties.